Gregor Mendel and Genetics
Important terms to know for Genetics
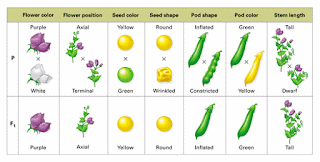
Punnett Square

Heredity and Genetics Vocabulary
Trait – A characteristic caused by genetics or
the environment
Chromosomes – Long strands of DNA that contain
thousands of genes
Genes – Part of chromosome that controls a trait(30,000
in humans)
Allele – Different forms of genes
Recessive
allele – Only see this
trait if two are present
Dominant Allele – Always shows its trait
Hybrid – Has two different alleles for same trait
Purebred – Has two identical alleles for same trait
Probability – The likelihood that an event will occur
Phenotype – The visibly expressed trait (ie. blue
eyes)
Genotype – The allele combination for a trait (ie.
Bb or bb.)
Homozygous – Two identical alleles (Purebred)
Heterozygous – Two different alleles (Hybrid)
Codominant
Alleles – Neither allele
is dominant(ie. Blood types or spotted dog)
Incomplete
Dominance – The dominant
alleles mix – (Green flower from blue and yellow alleles)
Meiosis – Process that creates sex cells with one
copy of each gene or half the number of chromosomes
Cross-Fertilization – A gamete(sex cell) from each parent
gives one allele for each trait to make a new organism(humans)
# of human
chromosomes – 23 pairs or
46 chromosomes
X and Y – Human chromosomes that determine gender
Mutation – When a chromosome is not copied
correctly
Carrier – Someone who has one recessive allele for
a trait but doesn’t show it.
Pedigree – A chart that tracts a particular trait
in a family
Karyotype - A
picture of all the chromosomes of a cell
Genome – All the DNA in one cell of an organism
Genotype – An analysis of a genome to determine
inherited traits

Comments
Post a Comment